Decorating for Halloween often means hanging fake cobwebs, cutting out scary bat shapes and spreading fake bugs, snakes and rats about the house. When we think of Halloween there are certain animals we associate with the spooky holiday—but what if these animals are just misunderstood?
Often our mistrust and disgust with the following creatures is simply due to our instincts that were instilled during the times of hunting and gathering, making us uncomfortable near animals and insects that may be venomous or dangerous. [1]
In honor of the spookiest season—October—we’re busting some myths surrounding traditionally “scary” creatures that deserve a smile just as much as any other cute creature.

Images via Field Trips Flickr
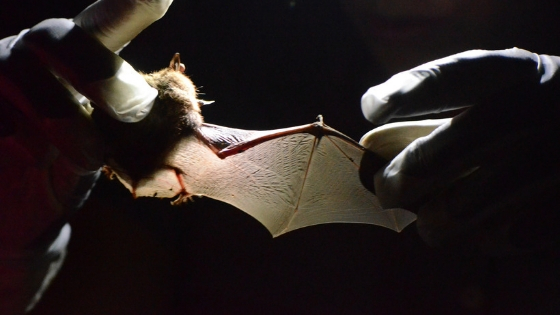
Myth 1: Bats want to drink your blood.
Bats are very misunderstood mammals that are a crucial part of Wisconsin’s ecosystem and wildlife. Bats eat a lot of pests that affect farmers’ crops as well as affect human’s well-being—helping to lower the spread of West Nile virus and other mosquito-borne illnesses. [2]
There are over 1,200 species of bats in the world, with only eight of those species being found in Wisconsin. [3] All of Wisconsin’s bats are insectivorous, meaning they eat only insects and NOT blood. Additionally, these eight are evening bats, meaning they come out during darker hours.
Bats are threatened.
All four species of cave bats in Wisconsin are state or federally threatened, and the four migrant tree bats are closely monitored to track population numbers. A large part of this is due to our misconceptions of bats as dirty, diseased and dangerous. The maltreatment and violence towards bats that appear in homes or buildings had wiped many out.
However, the single largest factor in rapid, significant bat decline is a disease called white-nose syndrome (WNS), which has caused up to 100% losses in some populations. WNS has caused the most significant decline of North American wildlife in recorded history
Additionally, bats face habitat loss and degradation, wind turbine related deaths, pesticide usage killing their food supply and disturbances during hibernation. [4]
How you can help.
There are several things the average Wisconsinite can do to protect bats:
- Educate your friends and family by sharing this article, as well as a positive attitude about bats.
- Build a bat house in your area.
- Avoid disturbing bat hibernation and roost sites.
- Safely evict bats from buildings and homes.
- Support the Wisconsin Conservation Fund.
- Get involved in citizen-based bat monitoring.

Images via Field Trips Flickr
Myth 2: Owls are spooky.
You know the scene: a spooky leaf-less tree branch creaks and shakes as the autumn wind howls. In the distance an owl screeches and lands in the tree, casting an eerie shadow lit by the full moon in back. While it may seem as if this moment has happened in almost every scary movie before something bad happens—the reality is that humans have no need to fear owls.
Owls have cool physical adaptations.
Wisconsin is home to 11 known species of owls: the Great Horned, Barn, Barred, Long-eared, Short-eared, Northern Saw-whet and Eastern-Screech Owls. [5] The Snowy, Northern Hawk, Great Gray and Boreal species of owls are visiting Wisconsin during the wintertime more and more due to “irruption” events caused by predator-prey interactions in their typical northern habitat. [6]
Owls’ ability to stick around for the winter is due to a few cool physical adaptations. First, their feet are covered with feathers that go all the way to the ends of their toes, keeping their feet nice and cozy during the chilliest time of the year. Second, owls have special body feathers that are extra-long to keep in extra heat. Their down coats and big wings keep them insulated against snow, rain and freezing winds. [7]
How you can help
Owls in Wisconsin face the perils of habitat loss and destruction as well as violence from farmers and humans looking to remove them from barns and garages, among other dangers. To help protect owls there are a few things you can do:
- Stop using rodent poison.
- Leave dead trees for owl roosting and nesting.
- Donate to the Wisconsin Bird Protection Fund.
- Watch your cat or dog closely or keep them on a leash when they are outside.
- Put up nest boxes or owl platforms.
- Remove items that could tangle up birds such as nets and barbed wire.
- Help your community become a Bird City.

Images via Field Trips Flickr
Myth 3: All Wisconsin snakes are venomous.
While the fear of snakes is understandable, there has only been one rattlesnake-related death in Wisconsin since 1900, making them significantly less dangerous than the white-tailed deer, which causes over 20,000 vehicle crashes annually. [8]
Wisconsin has 21 types of snakes, 19 being non-venomous and two being venomous, 14 of which are rare and listed as endangered, threatened or of special concern. [9] The two venomous species—the Timber rattlesnake and Eastern Massasauga Rattlesnake—live in very specific habitats in western Wisconsin and are endangered or of special concern, making an encounter with them very rare.
All snakes are cold-blooded—unlike mammals they do not rely on cellular metabolism to maintain their internal temperature, instead obtaining heat from external sources like the sun. Snakes are covered in scales that work as a sort of reverse raincoat—keeping water from leaving their body, preventing them from dehydrating. [10]
Snakes fear you.
Snakes are another supporter of Wisconsin’s agricultural community, reducing disease threats posed by rodents and keeping grain eating mammal populations low.
Like bats, fear of snakes has left them persecuted and under-appreciated for many years. Snakes do not strike unless provoked, rather using their defensive posture as a highly effective bluff. So, while it is possible to be bitten by a snake, they would much rather slither away to safety than fight, making avoidance of snakes the best protection. [11]
While avoidance is the best way, there are some ways you can tell the difference between a venomous and non-venomous snake: pupil shape, presence of a rattle and shape of the head. Stay away from snakes with elliptical pupils, rattles and triangular or arrow-shaped, wide heads. [12]
How you can help
There are several ways to help protect snakes in Wisconsin:
- Do not kill or harm snakes that you encounter.
- Educate your friends and family by sharing this article, as well as a positive attitude about snakes.
- Stop using rodent poison.
- Donate to the Wisconsin Amphibian and Reptile Conservation Fund.